For instance, rent is usually subject to a lease agreement that is relatively certain. Even though budget and actual numbers may differ little in the aggregate, the underlying fixed overhead variances are nevertheless worthy of close inspection. The variable overhead efficiency variance can be confusing as it may reflect efficiencies or inefficiencies experienced with the base used to apply overhead. For Blue Rail, remember that the total number of hours was “high” because of inexperienced labor.

Practice Video Problem 8-1: Computing direct materials variances LO2
If the outcome is favorable (a negative outcome occurs in the calculation), this means the company was more efficient than what it had anticipated for variable overhead. If the outcome is unfavorable (a positive outcome occurs in the calculation), this means the company was less efficient than what it had anticipated for variable overhead. This could be for many reasons, and the production supervisor would need to determine where the variable cost difference is occurring to make production changes. However, when used with other insights, variance analysis can guide companies through budgeting and financial management.
Labor Cost Variance
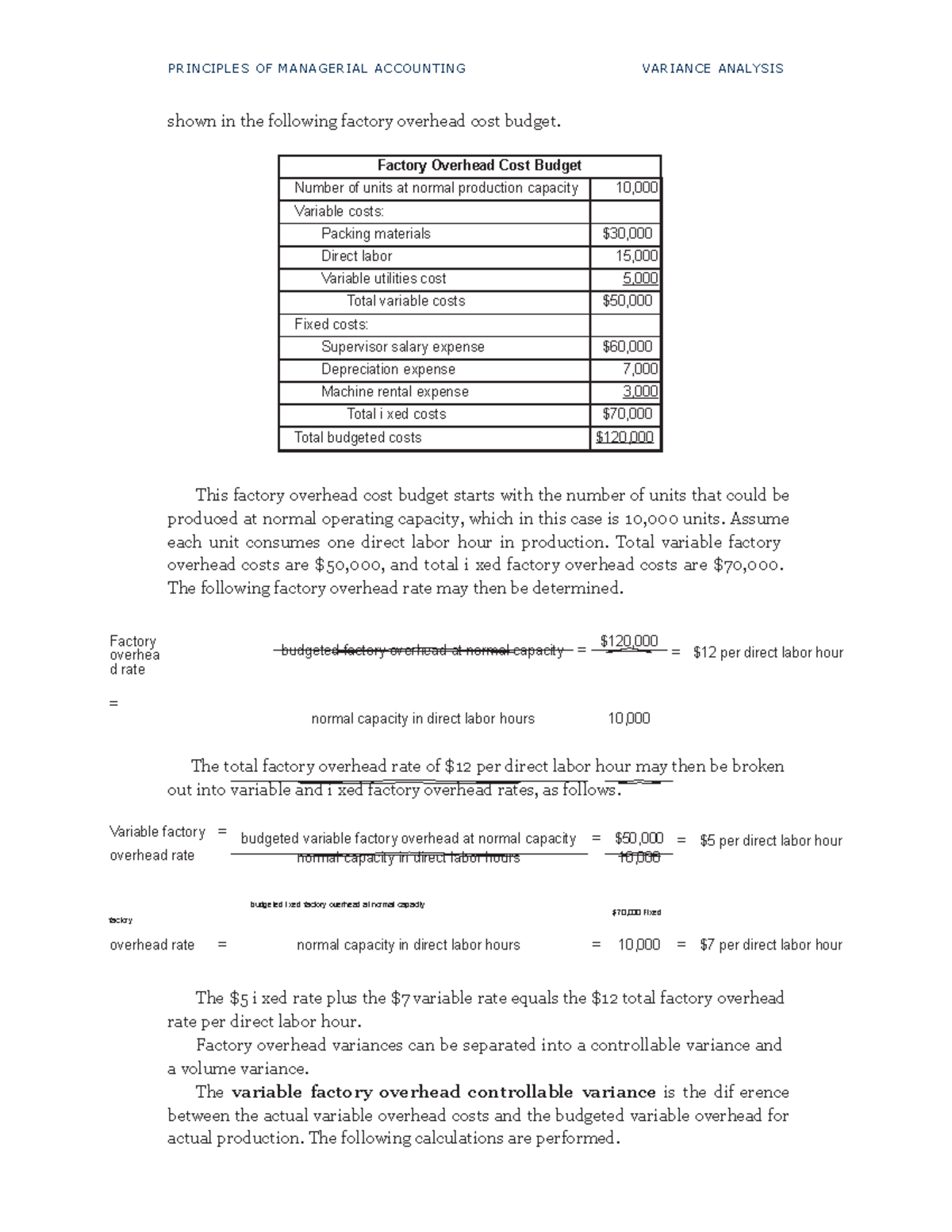
To reduce this possibility, performance should be measured on multiple outcomes, not simply on standard cost variances. Following is an illustration showing the flow of fixed costs into the Factory Overhead account, and on to Work in Process and the related variances. a cost that is easily traced to an individual cost object is called This reflects the standard cost allocation of fixed overhead (i.e., 10,200 hours should be used to produce 3,400 units). Notice that this differs from the budgeted fixed overhead by $10,800, representing an unfavorable Fixed Overhead Volume Variance.
Direct Material Price Variance:
As production occurs, overhead is applied/transferred to Work in Process (yyy). When more is spent than applied, the balance (zz) is transferred to variance accounts representing the unfavorable outcome. The completed top section of the template contains all the numbers needed to compute the direct materials quantity and price variances. The direct materials quantity and price variances are used to determine if the overall variance is a quantity issue, price issue, or both.
Due to the higher than planned hourly rate, the organization paid $22,500 more for direct labor than they planned. This variance should be investigated to determine if the actual wages paid for direct labor can be lowered in future periods or if the standard direct labor rate per hour needs to be adjusted. For example, an investigation could reveal that the company had to pay a higher rate to attract employees, so the standard hourly direct labor rate needs to be adjusted.
The Financial Modeling Certification
During the period, Brad projected he should pay $112,500 for variable manufacturing overhead to produce 150,000 units. Once the top section is complete, the amounts from the top section can be plugged into the formulas to compute the variable manufacturing overhead efficiency (quantity) and rate (price) variances. All standard cost variances are computed using the actual production quantity. As mentioned previously, standard rates and quantities are established for variable manufacturing overhead. When discussing variable manufacturing overhead, price is referred to as rate, and quantity is referred to as efficiency. Any variance between the standard costs allowed and the actual costs incurred is caused by a difference in efficiency or a difference in rate.
Direct Material Usage Variance measure how efficiently the entity’s direct materials are using. This variance compares the standard quantity or budget quantity with the actual quantity of direct material at the standard price. One must consider the circumstances under which the variances resulted and the materiality of amounts involved. One should also understand that not all unfavorable variances are bad. For example, buying raw materials of superior quality (at higher than anticipated prices) may be offset by reduction in waste and spoilage. Blue Rail’s very favorable labor rate variance resulted from using inexperienced, less expensive labor.
However, predicting and addressing variations brought on by circumstances beyond the company’s control is difficult. In closing this discussion of standards and variances, be mindful that care should be taken in examining variances. If the original standards are not accurate and fair, the resulting variance signals will themselves prove quite misleading. But, a closer look reveals that overhead spending was quite favorable, while overhead efficiency was not so good. Sure, it’s great that you’re doing better in said area than you predicted.
- Standard costs and quantities are established for each type of direct labor.
- The total variable manufacturing costs variance is separated into direct materials variances, direct labor variances, and variable manufacturing overhead variances.
- It is because fixed overheads do not usually change with activity levels.
- NoTuggins was featured as the most innovative new harness by the International Kennel Association.
- It is not sufficient to simply conclude that more or less was spent than intended.
Direct labor is considered manufacturing labor costs that can be easily and economically traced to the production of the product. For example, the direct labor necessary to produce a wood desk might include the wages paid to the assembly line workers. Indirect labor is labor used in the production process that is not easily and economically traced to a particular product. Examples of indirect labor include wages paid to the production supervisor or quality control team. While they are a part of the production process, it would be difficult to trace these wages to the production of a single desk.
As shown in Table 8.1, standard costs have pros and cons to consider when using them in the decision-making and evaluation processes. The proper use of variance analysis is a significant tool for an organization to reach its long-term goals. In the last section, we learned how variance analysis helps businesses. It helps them find trends, budget better, monitor finances, control costs, and make good choices.
